This lesson focuses mostly on discussing the idea of deviant behaviors in adolescence and how these behaviors are punished, mostly in the school setting. We will also continue our discussion on the upcoming projects, which for my second year students will be a persuasive speech.
First date taught: 9 Dec 2022
7A – Behaving Badly
Theme: Bad behavior at school and how to resolve it; persuasive speech structure and tips.
delinquent (n) – one who disobeys or breaks rules or laws
deviance (n) – actions or behaviors that violate formal and informal cultural norms such as law and the discouragement from public nose-picking
corporal punishment (n) – physical punishment, such as caning or flogging
corporal punishment (juvenile) – the deliberate infliction of physical pain by hitting, paddling, spanking, slapping, flicking, or any other physical force used as a means of discipline. The immediate aims of such punishment are usually to halt the offense, prevent its recurrence and set an example for others. The desired long-term goal is to change the child’s behavior and to make it more consistent with the adult’s expectations.
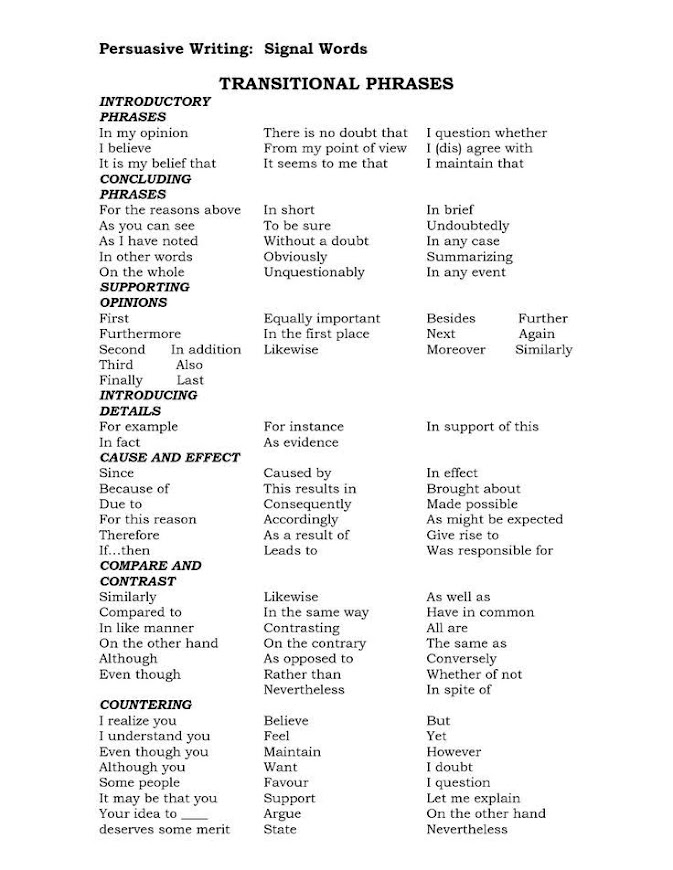
Persuasive Speaking
from the University of Pittsburgh, Department of Communication.
https://www.comm.pitt.edu/persuasive-speaking
Persuasive speaking is the type of speaking that most people engage in the most. This type of speech can involve everything from arguing about politics to talking about what to eat for dinner. Persuasive speaking is very connected to the audience, as the speaker must, in a sense, meet the audience halfway. Persuasion, obviously, is not entirely controlled by the speaker–persuasion occurs when an audience assents to what a speaker says. Consequently, persuasive speaking requires extra attention to audience analysis.
Traditionally, persuasion involves ethos (credibility), logos (logic), and pathos (emotion). By performing these three elements competently, a speaker can enhance their persuasive power.
Tips for Persuasive Speaking
Recognize that the audience is constantly processing what the speaker is saying. Nonverbal reactions are common for an audience listening to a persuasive speech–a furrowed brow, nodding head, or rolling eyes can be signals from audience members that they either like or dislike what the speaker is saying. Acknowledging these nonverbal reactions can help a speaker explain more in detail certain points.
Identify the target audience. In almost any persuasive speaking situation, there will be a subset of the audience that agrees, that disagrees, and that are undecided about the topic. Preaching to the choir–speaking to persuade those that already believe the speaker–might consolidate the audiences’ beliefs but has little benefit beyond that. Trying to persuade the segment of the audience that adamantly disagrees with the perspective voiced is generally unlikely (though not unheard of). Therefore, a speaker ought to focus on the part of the audience that is undecided on the issue. Speaking more directly to this group of undecideds allows a speaker to tailor their speech more towards their concerns.
Pre-empt common objections. Many audience members might be skeptical of the viewpoint advanced by a presenter. Consequently, an orator ought to acknowledge and respond to these objections within the speech. This approach might answer some of the questions that audience members might be asking of themselves.
Most persuasive speeches concern questions of fact, value, or policy. Issues of fact are similar to informative speeches in that they review findings. The difference is that persuasive speeches make judgments about which findings are accurate. Issues of value tackle the time-honored questions of what is good, right, or beautiful. Values can be either individually, communally, or nationally held, and are thus contentious and often clashing. Issues of policy concern what actions should be taken to resolve a particular problem. Policy questions posit a problem and a solution.
Articulate the goals of the speech. Does the speaker want the audience to sign a petition, write their legislator, boycott a product, talk to their friends, buy a certain product, or take some other tangible action? Oftentimes, the conclusion enables a speaker to make a call to action that is the culmination of a persuasive speech.
Additional Resources:





Attribution: Image by pressfoto on Freepik
